
Paper 4
Advanced Human Geography Options 1 hour 30 minutes
Candidates answer questions on two of the optional topics.
Each topic consists of one structured question (10 marks) and a
choice of essay questions (20 marks).
60 marks
– 25% of the total A level qualification.
13.1 Trade flows and trading patterns
Present for 4 minutes upon one of these topics (do not do the same one as each other!):
No single country can produce a can of coke
You could not build a toaster
There are still places on Earth that are difficult to get to
What is the difference between globalization, Westernization and ‘global interactions’? – watch the video below and answer this question.
Find definitions for the following key words:
| globalization | |
| interdependence | |
| multinational corporation | |
| protectionist measures | |
| free market | |
| domestic market | |
| capitalism | |
| IMF |
Globalization: A force for good or an evil monster?
Read the transcript of the podcast and complete the table in the download file above to include the positive and negatives of globalisation both currently and in the future. The two videos below will also help you complete this task.
Visible and invisible trade (imports and exports)
Trade refers to the exchange of goods and services for money.
The origin and continuing basis of global interdependence is trade. The global trading system developed at the time of European colonial expansion. Here, a ‘colonial division of labour’ emerged in which LICs exported primary products, agriculture and minerals, while Europe and North America exported manufactured goods.
This remained the general pattern of world trade until the post-second World War period, when a more complex pattern of international trade emerged. Trade is the most vital element in the growth of the global economy. World trade now accounts for over 30% of GDP – about 3 times the share in 1960.
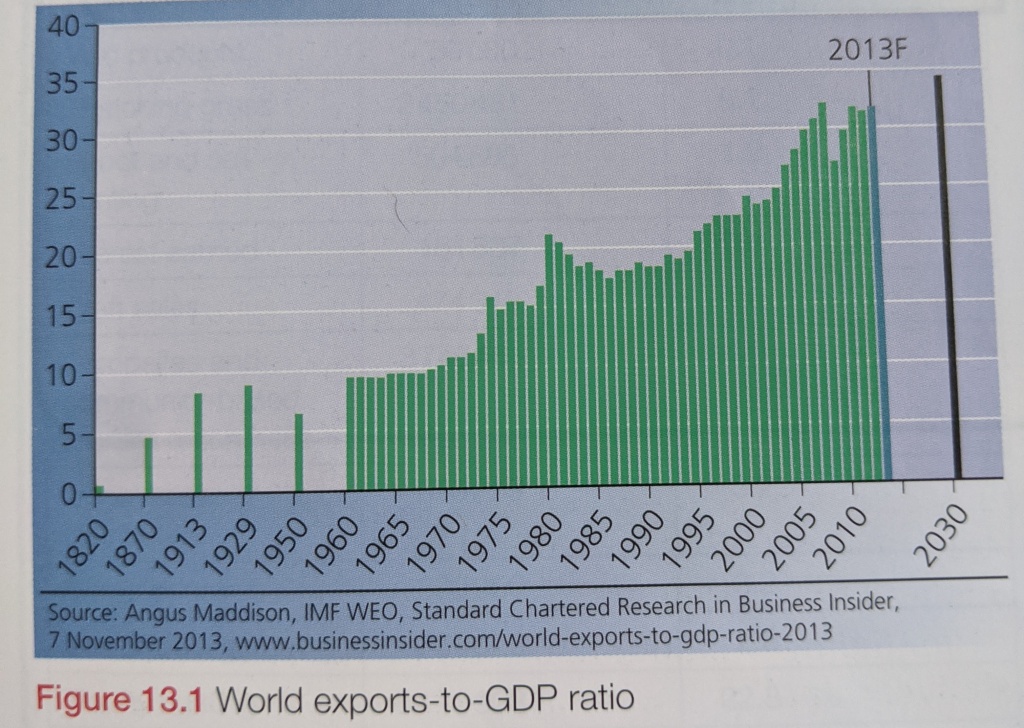
Trade results from the uneven distribution of resources over the Earth’s surface. Even countries with an abundance of resources and a wide industrial base cannot produce all of the goods and services that their populations desire. So they buy goods and services from other countries, providing that they have the money to pay for them. Goods and services purchased from other countries are termed imports. In contrast, goods and services sold to other countries are called exports.
Imports along with exports form the basis of international trade. The difference between the value of a country’s imports and exports is known as the balance of trade.
A trade deficit occurs when the value of a country’s imports exceeds the value of its exports. A country can make up this difference by using its savings or by borrowing, but clearly such a situation cannot continue indefinitely. In contrast, a positive or favourable balance is known as a trade surplus. A trade surplus contributes to the GDP of a nation, but a trade deficit will reduce GDP.
GDP – Gross Domestic Product = the final value of the goods and services produced within the geographic boundaries of a country during a specified period of time, normally a year.
Visible trade involves items that have physical existence and can actually be seen. Thus raw materials (primary products) such as oil and food, and manufactured goods (secondary products) such as cars and furniture, are items of visible trade.
Invisible trade is trade in services which include travel and tourism and business/financial services.
Global patterns of and inequalities in trade flows
Write a description of what the graph below shows:

Answer: The figure above shows the growth in the value of global trade in goods (merchandise) and services between 2003 and 2013. The value of the global trade in goods increased from less than $8 trillion in 2003 to more than $18.5 trillion in 2013. Trade in services also increased significantly from about $2 trillion in 2003 to about $4.7 trillion in 2013. For both the start and end years the value of world trade in services was roughly a quarter that of global trade in goods. The severe dip in the trade in goods in 2008-9 indicates the strong effect of the global financial crisis on world trade. The dip in the trade in services was of a much lower magnitude.
Factors affecting global trade – see textbook
The World Trade Organisation, International Monetary Fund and World Bank
Watch this video to understand how the WTO, IMF and World Bank work:
AIM:
To examine the influence of world trading organizations and financial institutions (such as the World Trade Organization, International Monetary Fund and World Bank) in the transfer of capital.
Task 1: Who are these ‘world trading organizations and financial institutions’? – make notes on each of the 3 organisations using the following information and your own research:
https://www.wto.org/english/thewto_e/whatis_e/tif_e/fact1_e.htm – World Trade Organisation (WTO)
https://www.imf.org/en/About – International Monetary Fund (IMF)
https://www.worldbank.org/en/about/what-we-do – World Bank
Take the twitter challenge … answer the question ‘What is the WTO | IMF | World Bank?’ in 140 characters or less.
Watch the peanut video (great song!!) and complete the worksheet below – it will be easier to do this as you go along rather than watch the video and try to remember the answers.
Task 2: How do these ‘world trading organizations and financial institutions’ influence transfers in capital?
https://www.theguardian.com/world/1999/mar/05/eu.wto3 – make notes from this story about the trade war that developed in relation to bananas that could be used as a case study.
https://www.theguardian.com/business/2016/jul/23/imf-calls-for-more-government-spending-as-rate-cuts-lose-their-impact (You will need to register to read this – it’s free though!) Why does the IMF need governments to spend more money on developing infrastructure?
Use the following video about Morocco to get some case study information about how the World Bank works:
This article is 10 years old. Have a read and then see if you can find out if the situation is still the same or if things have improved.
Complete the following exam questions:
Assess the strengths and limitations of the work of the World Trade Organization (WTO). [20]
Fairtrade
https://www.fairtrade.net/about/what-is-fairtrade Use the website to write your own functional definition of fairtrade, and note some of the key benefits of fairtrade.

Some of the most famous fairtrade products are chocolate, bananas and coffee:




Complete the exam questions below:
One thought on “Human Geography Options: Global Interdependence”